افعال حالتی در انگلیسی
What is a stative verb?
A stative verb is a type of verb that describes a state of being or perception. Stative verbs can refer to mental (e.g., “believe”) or emotional states (e.g., “dislike”), as well as physical states or qualities (e.g., “contain”).
Stative verbs can be used to express possession, opinions, emotions, senses, and other states like measurement, cost, and weight.
Stative verbs examples
A water molecule consists of three atoms. [possession]
I don’t think they will win the election. [opinion]
She hates working on the weekends. [emotion]
The dog smelled really bad after the rain. [sense]
This jacket costs a lot. [cost]
How to use stative verbs
It’s important to keep in mind that stative verbs describe situations that are unlikely to change. Due to this, stative verbs are typically not used in continuous tenses (i.e., with verbs ending with “-ing”), such as the present continuous and the present perfect continuous. However, there are some exceptions, such as the verb “feel” (e.g., “I’m not feeling good”).
Examples: How to use stative verbs
He is knowing exactly what needs to be done.
He knows exactly what needs to be done.
Stative verbs are often intransitive verbs, meaning they don’t take a direct object. Intransitive verbs are often followed by modifiers, like adverbs or prepositional phrases, that provide additional information.
Examples: Intransitive stative verbs
This cake smells delicious.
I felt sick this morning.
Cheryl was here.
However, some stative verbs can also be transitive and take a direct object such as a noun or pronoun.
Examples: Transitive stative verbs
I love that movie.
He owns several vinyl records.
She really likes you.
Stative verbs vs. action verbs
Stative verbs are often contrasted with action or dynamic verbs. While stative verbs indicate a situation or state of being, action verbs describe what the subject of the sentence is doing or has done. Action verbs can refer to both physical and mental actions (e.g, “he ran,” “I’m thinking”).
Some verbs can be either stative or dynamic depending on the meaning of the sentence. For example, the verb “see” can denote an opinion (stative verb), or the physical action of meeting with someone (action verb).
Examples: Stative vs. action verbs
I don’t see any problem with that.
They’ve been seeing each other for a month now.
One way to distinguish stative verbs from action verbs is to look at the verb tense. Stative verbs are never used in the continuous tenses, while action verbs can be used in all verb tenses.
Stative verbs vs. linking verbs
Stative and linking verbs are both used to add more information about the subject of a sentence. Many verbs can be considered as both linking and stative, such as the sense verbs “taste,” “smell,” and “feel.”
However, not all stative verbs are linking verbs. While stative verbs can be transitive, meaning they take a direct object, linking verbs are not transitive. Linking verbs are always followed by a subject complement (i.e., a noun, pronoun, or adjective that describes the subject).
Examples: Stative verbs vs. linking verbs
I like vanilla ice-cream.
I feel tired.
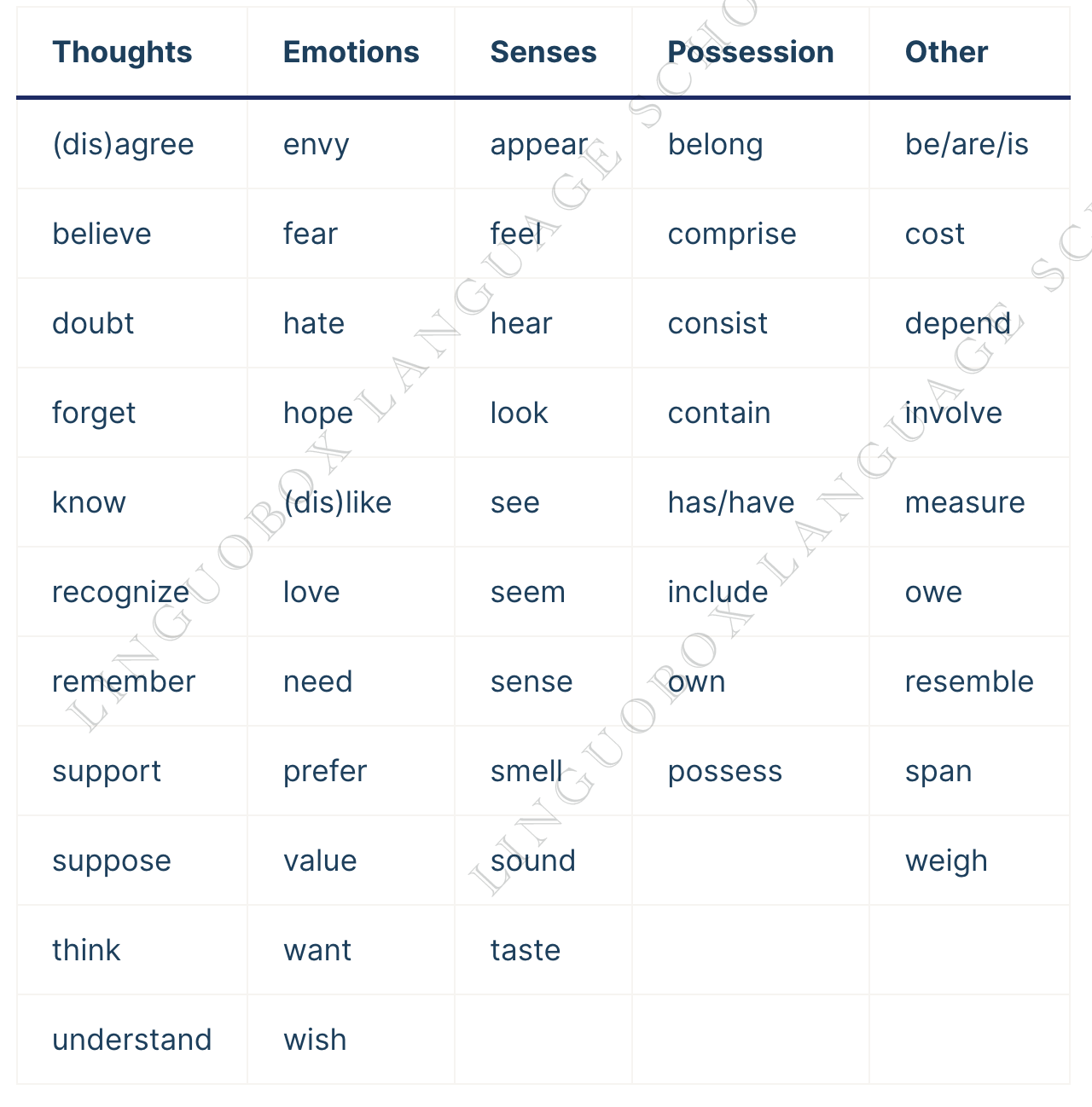
Stative verbs list
Here is a list of common stative verbs:
| Thoughts | Emotions | Senses | Possession | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dis)agree | envy | appear | belong | be/are/is |
| believe | fear | feel | comprise | cost |
| doubt | hate | hear | consist | depend |
| forget | hope | look | contain | involve |
| know | (dis)like | see | has/have | measure |
| recognize | love | seem | include | owe |
| remember | need | sense | own | resemble |
| support | prefer | smell | possess | span |
| suppose | value | sound | weigh | |
| think | want | taste | ||
| understand | wish |
| like | know | belong |
| love | realise | fit |
| hate | suppose | contain |
| want | mean | consist |
| need | understand | seem |
| prefer | believe | depend |
| agree | remember | matter |
| mind | recognise | see |
| own | appear | look (=seem) |
| sound | taste | smell |
| hear | astonish | deny |
| disagree | please | impress |
| satisfy | promise | surprise |
| doubt | think (=have an opinion) | feel (=have an opinion) |
| wish | imagine | concern |
| dislike | be | have |
| deserve | involve | include |
| lack | measure (=have length etc) | possess |
| owe | weigh (=have weight) |
